Laboratory analysis
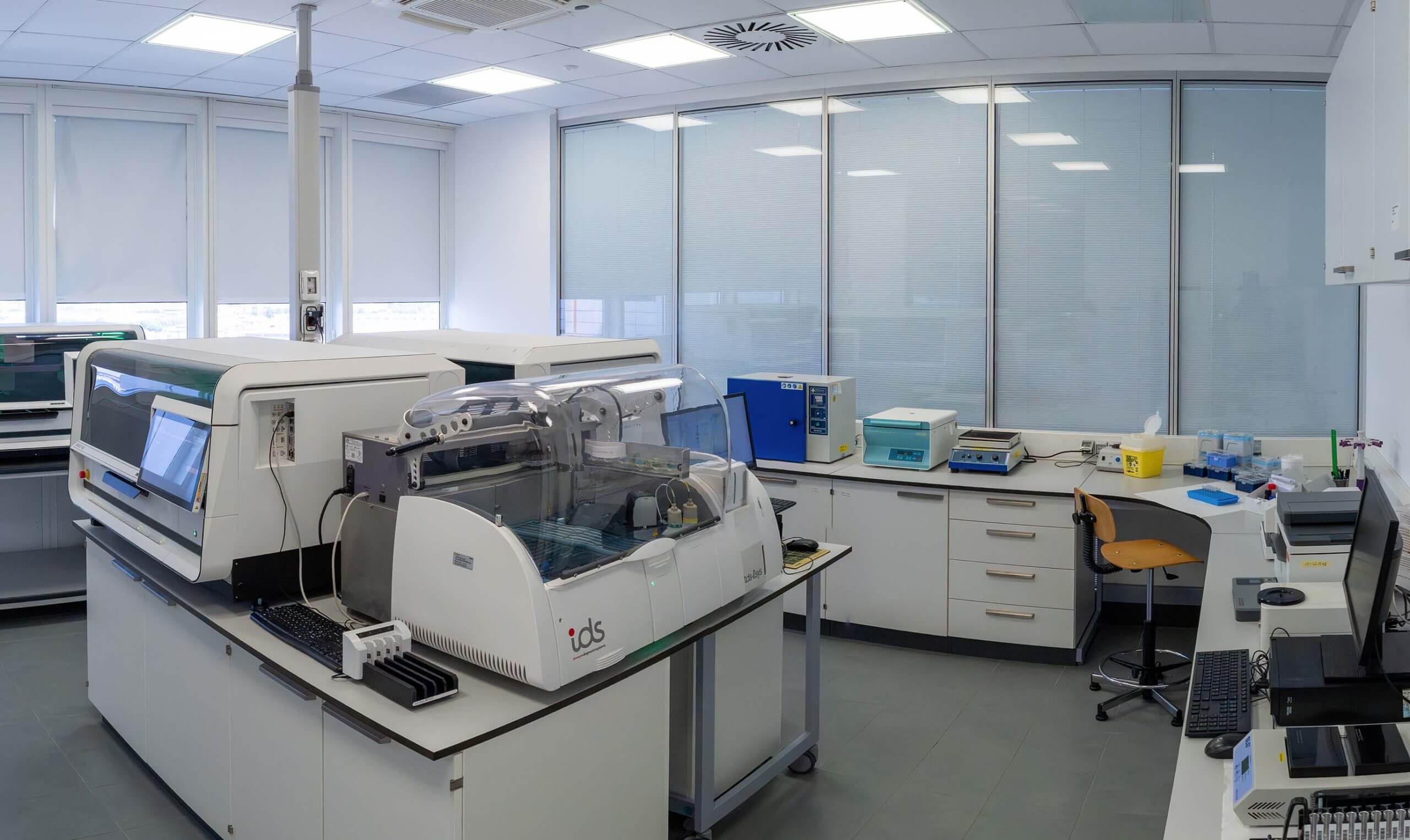

From research to diagnosis: the laboratory where quality and reliability merge.
Anti-Th/To Antibodies
Test for the determination of human antibodies of the immunoglobulin class IgG against the RNase MRP macromolecular complex (anti-Th/To), to support the diagnosis of systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARD), particularly systemic sclerosis (SSc).
Anti–SS-B/La Antibodies
Test for the determination of human antibodies of the immunoglobulin class G against the SS-B/La antigen, to support the diagnosis of systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARDs), particularly Sjögren’s syndrome (SjS), and assessing the risk of neonatal lupus and congenital heart block.
Anti-Ro52 kDa Antibodies
SARDs are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by dysregulation of the immune system, that starts to turn against the body’s own tissues. Major SARDs include systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic sclerosis and Sjögren’s syndrome. These diseases can affect multiple organs and share common symptoms such as fatigue, fever, joint pain and skin rash. Diagnosis relies on a combination of clinical assessment and specific autoantibody tests. Early diagnosis is crucial to initiate appropriate therapy and slow down disease progression. The term anti–SS-A/Ro refers to autoantibodies targeting two distinct antigens: Ro60, a 60 kDa protein associated with non-coding RNA, and Ro52 (TRIM21), a 52 kDa cytoplasmic E3 ubiquitin ligase. The presence of anti-Ro/SSA antibodies (without distinguishing between Ro60 and Ro52) is included in the classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome (SjS), although they are not exclusive to this condition. Concomitant positivity for Ro60 and Ro52 is strongly associated with SjS, whereas isolated Ro60 positivity is more commonly observed in SLE. Isolated Ro52 positivity is less specific for SjS and may be detected in several conditions, such as autoimmune myopathies, systemic sclerosis and interstitial lung diseases. Distinguishing between anti-Ro52 and anti-Ro60 is therefore clinically relevant, as each autoantibody may be associated with different clinical phenotypes and specific systemic manifestations.
Anti–SS-A/Ro Antibodies
Test for the determination of human antibodies of the immunoglobulin class IgG against the SS-A/Ro antigens (Ro52 and Ro60), to support the diagnosis of systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARDs), particularly Sjögren’s syndrome (SjS) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Anti–SS-A/Ro60 Antibodies
Test for the determination of human antibodies of the immunoglobulin class IgG against the SS-A/Ro60 antigen, to support the diagnosis of systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARDs), particularly Sjögren’s syndrome (SjS) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Anti-SRP Antibodies
Test for the determination of human antibodies of the immunoglobulin class IgG against the SRP complex (anti-SRP), to support the diagnosis of systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARD), particularly myositis.
Anti–Sm (Smith) Antibodies
Test for the determination of human antibodies of the immunoglobulin class IgG against the Sm (Smith) antigen, to support the diagnosis of systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARDs), particularly systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Anti-SLA/LP Antibodies
Test for the determination of human antibodies of the immunoglobulin class IgG against the Soluble Liver Antigen/Liver–Pancreas antigen (SLA/LP), to support the diagnosis of autoimmune liver diseases, particularly autoimmune hepatitis (AIH).
laboratory
From research to diagnosis: the laboratory where quality and reliability merge.
Discover what’s new
Subscribe to the newsletter
Subscribe to our newsletter to be always updated.